Impulse Control Disorder can make everyday situations feel overwhelming, especially when sudden urges lead to actions that are hard to stop. It affects teens and adults who struggle to pause, think, and choose a safer response. This condition is more than “acting out” — it’s a real challenge that disrupts school, relationships, and emotional well-being. With the right support, individuals can learn to manage impulses, recognize triggers, and build healthier habits. Understanding the root cause is the first step toward real change. Whether it’s anger, risk-taking, or compulsive behaviors, help is available. Early awareness and treatment can make a powerful difference in long-term growth and stability.
What is Impulse Control Disorder?
Impulse control disorder occurs when an individual cannot self-regulate, and when they understand that they might do something that might be harmful or problematic. It influences the brain capacity to control urges; hence, the individual will take action in a very fast manner without considering the outcomes. Such conditions may include such behaviors as abrupt anger, embezzling, gambling, or self-injury. It may complicate everyday life since the individual experiences overwhelming desires that control their behaviors.
Through appropriate guidance, one is able to realize these urges and to know healthy means of dealing with them. Therapy makes the individual take their time and think better so as to make safer decisions. Medical therapy can also be used to manage stress and emotions. Once a person reaches out for a helping hand, they begin to regain control of their life and become more balanced.
Impulse Control Disorder Symptoms
Here are the signs of impulse control disorder:
- Experiencing strong desires that are difficult to restrain.
- The instant action without considering the outcomes.
- Sustaining stressful or problematic behavior.
- Experiencing guilt or sadness following the action, yet repeating it.
- Difficult to control emotions in everyday life.
- Engaging in fights at home, school, or work due to hasty behavior.
Impulse Control Disorder Causes
The causes of impulse control disorder may be a complex of factors:
- Brain chemistry: The impulsiveness can be due to changes in chemicals that regulate feelings and urges.
- Genetics: There may be a family history of mental illnesses that predisposes the risk.
- Stress and trauma: Attention to stressful situations or trauma may provoke impulsive responses.
- Personality: More actively thrill-seeking or frustrable individuals might have problems with impulse control.
- Additional mental disorders: Anxiety, depression, or ADHD may be involved in impulse control problems.
What is an Example of an Impulsive Behavior?
- Acting without thinking and shouting.
- Taking a gamble and thinking of the results.
- Ingesting or sipping excessively on impulse.
- Suddenly interrupting or talking out of turn.
- Taking up risky behavior without planning.
7 Types of Impulse Control Disorders
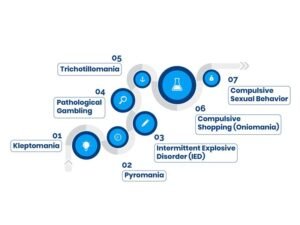
1-Kleptomania
Kleptomania leads to a great desire to steal objects, even without any necessity. The act brings relief or excitement that lasts only temporarily, but it is usually accompanied by guilt and law problems. Humans find it difficult to resist temptation,n and theft could become a habit. These impulses can be controlled with the help of therapy. Drugs can also help with stress and urge management.
2-Pyromania
The nature of pyromania is an uncontrolled desire to make fire. Individuals experience stress before setting fire, and relief or excitement after doing so. Such conduct may present very severe damage to themselves and other people. They also repeat the act, although they are aware of the dangers. The goal of treatment is on treatment and education on how to safely respond to urges.
3-Intermittent Explosive Disorder (IED)
Intermittent Explosive Disorder causes an individual to experience sudden outbursts of anger. In an unplanned manner, they can yell, strike, or even demolish property. Such episodes may damage relationships, lead to legal or workplace issues. Counseling can make people calm down and use their brains. Extreme mood swings can also be worked through medication.
4-Pathological Gambling
Pathological Gambling is the reason that develops an irresistible desire to gamble even when one loses money or suffers severe repercussions. Before gambling, the individual experiences stress, a nd after gambling, the person experiences relief. It usually has an impact on money, marriage, and work. Healthy coping techniques are learned during therapy. Drugs can be used to decrease urges.
5-Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania causes an individual to remove their hair either on the head, eyebrows, or any other parts. It relieves stress in the short term but may result in hair loss and emotional disturbances. Individuals experience guilt or shame and can not quit. Therapy assists in substituting the habit with more harmless activities. Urges may be managed by the use of support and medication.
6-Compulsive Shopping (Oniomania)
Compulsive Shopping causes one to develop a desire to purchase what they do not require. Purchasing offers short-lived joy, yet it frequently results in debts and frustration. You find it hard, even when they are aware that it is negatively affecting their life. These impulses can be controlled using therapy and budgeting plans.
7-Compulsive Sexual Behavior
Compulsive Sexual Behavior makes an individual respond to sexual urges excessively and uncontrollably. It may damage relationships, work, and personal life. Individuals can be ashamed or guilty of doing things out of impulse. Therapy assists in the creation of healthy coping mechanisms. In other instances, a medication may be used to diminish the level of urgency.
Does ADHD Affect Impulse Control?
Yes, ADHD affects impulse control because people with ADHD often act quickly without thinking. They may interrupt others, make sudden decisions, or take risks without considering the results. Their brain struggles to manage attention and self-control, so impulses feel stronger and harder to resist. This makes daily life challenging at school, work, or in relationships.
However, people with ADHD can learn to manage impulses with support. Therapy helps them pause, think, and make better choices. Medication can also improve focus and reduce impulsive actions. With practice and guidance, people with ADHD gain more control over their behavior and feel more confident in daily life.
Teen Impulse Control Disorder Treatment
Impulse Control Disorder Test
The first thing to start with in our team is a thorough testing to get to know the patterns of behavior of your teen. The impulsive tendencies are identified by way of questionnaires, observation, and interviews. Early diagnosis helps in distinguishing impulse control problems from any other mental illness. The plan of treatment is based on accurate results. This will provide your teen with proper support.
Initial Evaluation
The first assessment will involve a full examination of the medical history of your teen and their behavioral patterns. Our specialists interview teens and family members. Social, academic, and emotional functioning are evaluated as well. This action can be used to determine triggers and challenges unique to your teenager. An in-depth assessment is the basis of effective treatment.
Medication Management
Drugs may also be used to treat impulsivity and enhance emotional regulation in certain situations. Our staff is keen on prescribing and monitoring treatment to make it safe and effective. Progress and side effects are monitored with frequent follow-ups. The combination of medication and therapy gives the most successful outcomes. This will enable the teens to have more control over their impulses.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT can help teens identify the causes and reasons of impulsive actions. During organized classes, they get to know how to cope and solve their problems. CBT promotes behavior and emotional change. Teens are taught techniques in actual life scenarios. This treatment is a long-term self-regulation and self-confidence.
Lifestyle Changes
Exercise habits are important in controlling impulses. Exercise, healthy eating, and sleep make people happier. Temptations are controlled by stress-reduction practices such as mindfulness or journaling. Reduction in screen time and social activities is are aid to good behavior. Lifestyle changes, supplement therapy, and drug effects.
Final Thoughts
The Impulse Control Disorder (ICD) influences the ability to resist urges by the individual, usually causing the performance of activities that may be harmful to the individual or others. It can affect the relationships, work, and the general well-being. Early diagnosis of symptoms like sudden anger, compulsive gambling, or kleptomania will aid in the treatment of the disorder. Therapy, typically cognitive-behavioral, is usually used to help individuals learn about triggers and acquire healthier coping mechanisms.
In others, drugs can help to regulate impulses and stabilize mood. Other factors that are important to recovery are lifestyle change, stress management, and good social support. Those individuals with ICD are able to live active lives, and with proper guidance and care, they can lead a normal life. To learn more, Mental Behavioral is a trustworthy source of information about impulse control disorder and its treatment.
FAQs
What is Impulse Control Disorder?
Impulse Control Disorder is a mental health condition where a person struggles to resist urges or impulses that may harm themselves or others, such as gambling, stealing, or sudden aggression.
What causes Impulse Control Disorder?
ICD can develop due to a mix of genetic, biological, and environmental factors. Stress, trauma, or certain brain imbalances may increase the risk of developing this disorder.
What are common symptoms of ICD?
Symptoms include sudden urges to act without thinking, irritability, aggression, compulsive behaviors like gambling or shopping, and difficulty controlling emotions or actions.
How is Impulse Control Disorder treated?
Treatment often includes therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, medications for mood stabilization, lifestyle changes, and support from family or support groups.
Can people with ICD live a normal life?
Yes, with proper treatment, support, and coping strategies, individuals with ICD can manage impulses effectively and lead balanced, fulfilling lives.








