Delusional disorder is a complex mental health condition that affects the way a person thinks, feels, and understands reality. It creates strong beliefs that do not match facts, yet these beliefs feel completely real to the individual. As a result, daily life, relationships, and emotional balance may feel stressful and confusing. However, many people with this condition continue normal routines, which often makes the disorder hard to notice. Over time, constant worry, fear, or mistrust may grow and affect mental well-being.
Therefore, early awareness and proper care play an important role in recovery. With the right guidance, support, and treatment, people may manage symptoms and regain emotional stability. Mental Behavioral highlights the importance of understanding delusional disorder to promote better mental health and overall quality of life.
What is delusional disorder?
Delusional disorder is a mental health condition where a person strongly believes in things that are not true. These false beliefs, called delusions, seem real to the person even when there is clear evidence against them. For example, someone may think that people are spying on them, or that they have a special relationship with a famous person. Unlike other mental illnesses, people with delusional disorder usually act normally in daily life, and their thinking and behavior outside the delusion remain clear.
However, these delusions can cause serious problems in relationships, work, and social life. In addition, people with this disorder may feel anxious, angry, or suspicious because of their false beliefs. Therefore, it becomes important to seek help early. Treatments like medication and therapy help reduce the intensity of delusions and improve overall well-being.
Delusional Disorder Symptoms
Here are the common symptoms of delusional disorder:
- Strong and persistent false beliefs that feel real
- Constant suspicion or mistrust of others
- Feelings of anger or irritation when someone disagrees
- Problems keeping relationships because of unusual beliefs
- Feeling anxious, tense, or on edge because of the beliefs
- Acting normal in daily life except when the belief appears
Types of Delusional Disorder
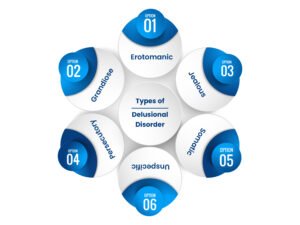
Erotomanic
People with this type believe that someone, often famous or of higher social status, is secretly in love with them. They may try to contact the person through letters, gifts, or calls. This can lead to persistent stalking behaviors. Despite clear evidence, they remain convinced of the love. It can cause emotional distress and legal problems if boundaries are crossed.
Grandiose
In this type, the person believes they have exceptional abilities, wealth, fame, or special knowledge. They may have a unique mission or be chosen for an important purpose. This delusion is not supported by reality but feels real to them. They may exaggerate their achievements or talents to others. Such beliefs can impact relationships and decision-making.
Jealous
Individuals believe their spouse or partner is unfaithful without any proof. They constantly check, accuse, or spy on their partner. The delusion can lead to controlling or aggressive behavior. Even reassurance or evidence does not change their conviction. This type often causes severe relationship strain and emotional tension.
Persecutory
People think they are being harmed, conspired against, or watched by others. They may believe neighbors, coworkers, or strangers are plotting against them. This is the most common type of delusional disorder. It can cause distrust, anxiety, and sometimes legal disputes. Their behavior may seem suspicious or defensive to others.
Somatic
Individuals believe they have a physical defect, disease, or abnormality that doctors cannot detect. They may frequently seek medical care despite negative test results. The delusion can lead to significant worry and preoccupation with the body. They may avoid social situations due to embarrassment. This type can also coexist with actual physical health concerns.
Unspecific
Delusions do not fit any of the recognized categories. They may be unusual, bizarre, or changing in nature. The person may hold strong false beliefs that are difficult to categorize. These delusions still impact behavior and daily life. Treatment focuses on reducing distress and improving insight.
What Causes Delusional Disorder?
Here are the common causes of delusional disorder in simple words:
- Differences in how the brain works can affect thinking and perception
- An imbalance of certain brain chemicals may play a role
- A family history of mental illness can increase the risk
- Traumatic or highly stressful events may trigger false beliefs
- Certain personality traits, like suspiciousness or sensitivity, may make a person
- Spending a lot of time alone can increase vulnerability to false beliefs
Delusional Disorder Examples
Here are some common examples of delusional disorder:
- Believing that someone constantly watches or follows them, even without proof
- Thinking that a famous person is secretly in love with them
- Believing that a spouse or partner is cheating, even when there is no evidence
- Feeling that people plot against them or try to harm them
- Thinking that they have a special mission or power that others do not understand
- Believing that a stranger or neighbor sends secret messages just for them
Delusional Disorder Vs Schizophrenia
Delusional disorder and schizophrenia are both mental health conditions, but they differ in important ways. In delusional disorder, a person has strong false beliefs that feel real, yet they can act normally in daily life outside these beliefs. In contrast, schizophrenia affects thinking, emotions, and behavior more widely. People with schizophrenia may see or hear things that are not real, have disorganized thoughts, and struggle to perform daily tasks.
However, both conditions can cause serious problems in life, like difficulties in relationships or work. Delusional disorder usually focuses on specific false beliefs, while schizophrenia affects many areas of thinking and perception. Therefore, understanding these differences helps doctors provide the right treatment. With therapy, medication, and support, individuals with both conditions can effectively manage their symptoms and enhance their overall quality of life.
How does Delusional Personality Disorder affect Mental Health?
Delusional Personality Disorder strongly impacts mental health because it shapes how a person thinks, feels, and reacts to the world. A person holds fixed beliefs that do not match reality, and these beliefs guide daily decisions. As a result, stress, fear, and confusion often rise. The mind stays alert for threats that do not exist, which increases anxiety and emotional tension. Over time, this constant mental pressure reduces peace of mind and emotional balance.
Moreover, this condition also harms relationships and social well-being. The person may mistrust family, friends, or coworkers, which leads to isolation and loneliness. Therefore, support systems become weak, and emotional health suffers more. In addition, work life and daily routines become difficult because focus and judgment feel unstable. However, with proper mental health care, guidance, and support, a person can manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Delusional Disorder Treatment
Medication Management
Medication helps reduce the intensity of delusional thoughts and emotional distress. Antipsychotic medicines support clearer thinking and better emotional control. In many cases, doctors also add anxiety or mood medications to improve stability. As treatment continues, symptoms often feel less overwhelming. With regular follow-ups, medication supports long-term mental balance.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy focuses on improving thinking patterns and emotional responses. A therapist helps the person question beliefs in a safe and supportive way. Over time, trust develops, which makes therapy more effective. In addition, sessions teach coping skills for stress and daily challenges. This approach supports better emotional awareness and control.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps a person understand the link between thoughts, feelings, and actions. The therapist guides the person to examine delusional beliefs gently. As a result, emotional reactions become more manageable. This therapy also strengthens problem-solving skills. Therefore, daily functioning and confidence often improve.
Family Education and Support
Family support plays an important role in recovery. Education helps loved ones understand the condition and respond calmly. As families learn better communication skills, conflicts reduce. Moreover, emotional support creates a stable environment. This support improves treatment outcomes and emotional well-being.
Lifestyle and Stress Management
Healthy routines support mental stability and emotional health. Regular sleep, balanced meals, and light exercise reduce stress levels. In addition, relaxation techniques help calm the mind. Avoiding alcohol and drugs also protects mental clarity. Over time, these habits strengthen overall treatment results.
Final Thoughts
Delusional Disorder affects thoughts, emotions, and daily functioning, but effective treatment offers hope and stability. With the right combination of medication, therapy, and emotional support, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and enhance their overall quality of life. Early care plays a key role because it helps reduce stress, confusion, and social difficulties. Moreover, consistent treatment builds trust, emotional balance, and healthier thinking patterns. Family involvement and healthy lifestyle choices also support long-term progress.
Reliable information and professional care empower individuals to take control of their mental well-being. For trusted insights, awareness, and guidance on mental health conditions, Mental Behavioral serves as a reliable source of information. With understanding, patience, and structured care, individuals can move toward emotional stability and a more fulfilling life.
FAQs
What is delusional disorder?
Delusional disorder is a mental health condition where a person holds strong beliefs that do not match reality. These beliefs feel true to the person and may affect thoughts, emotions, and daily life.
What are common signs of delusional disorder?
Common signs include fixed false beliefs, strong mistrust, constant worry, and emotional stress. However, daily behavior may still appear normal in many situations.
What causes delusional disorder?
Stress, trauma, family history, and chemical changes in the brain may play a role. Life pressure and emotional strain may also increase the risk.
How does delusional disorder affect mental health?
It may increase anxiety, isolation, and emotional tension. Over time, it may affect relationships, work, and overall mental well-being.
Can delusional disorder be treated?
Yes, treatment may help manage symptoms. Medication and regular mental health support may improve thinking patterns and emotional balance.





